APT stands for the asset protection fund is a legal document that allows a third-party trustee to hold items of value and keep them away from judgment creditors. The document on which the trust is written is the deed of trust. The trustee must act under the terms of the trust deed. In general, the trustee has a duty to carry out the settlor's intent. The trustee acts as the trustee for the beneficiaries of the trust. Thus, the purpose of an asset protection fund is to keep assets out of the hands of creditors. We compare offshore and domestic options. These types of funds are available in several US states such as Nevada, Delaware and Alaska. Foreign countries such as the Cook Islands, Nevis and Belize offer some of the most protective statutes.
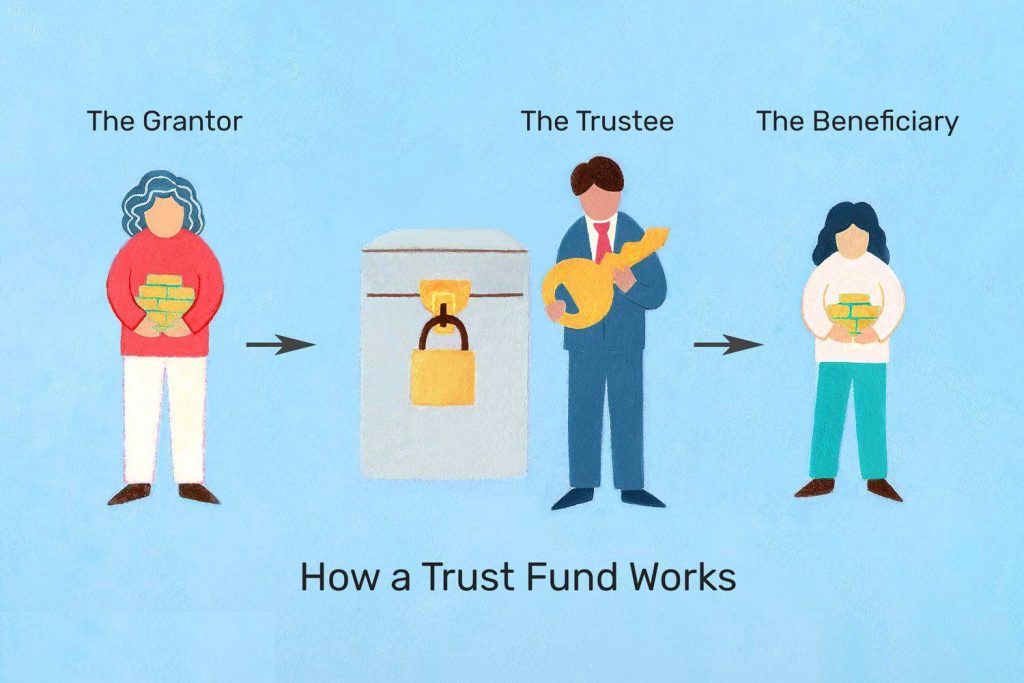
The assets within the trust are out of reach of the trust beneficiary's creditors. The beneficiary is usually the one who is entitled to receive money from the trust. In this case, the creditor is the one who won the lawsuit against you. The settlor is the one who establishes the trust. Here you will find more information about what an asset protection trust is and how it works.
When you establish the trust, you decide whether or not you will also be a beneficiary of the trust. We also set up non-self-established trusts, such as children's trusts. As the name implies, we build this kind of trust for the benefit of your children. Jurisprudence has shown that neither your creditors nor those of your children can touch fiduciary assets. You can access trust funds by obtaining a fund loan. Then we also establish self-established trusts where you establish the trust and maintain beneficial interest in the trust.
Certain jurisdictions are more favorable than others. Examples are offshore trusts that include countries such as the Cook Islands, Nevis and Belize. Favorable US states include Nevada, South Dakota, Delaware, and Alaska. There, you can form the trust, maintain beneficial interest, and statutorily enjoy protection from seizure.

The formal definition of this concept sounds quite simple. A trust fund is one of the types of investment funds (Investment Fund), its main task is to guarantee the transfer of property and assets to the disposal of a specific person. If the meaning of the concept has escaped you, we can offer another definition.
A trust fund is a type of formal agreement that allows private (individual) persons to benefit in favor of another person or entity. And if this option does not suit you, we can offer a third one. A trust fund is a business instrument / organization that assumes legal obligations to manage / manage any assets or valuable property of an individual or legal entity for the purpose of making a profit.
If, however, we set the task to finally understand the definitions, dotting all the "i", then we will get bogged down in terms, features of their translation from English and law enforcement practice. But it is better to do this right away - this will allow you to continue to speak as specifically as possible, avoiding inaccuracies and errors.
Similar and related concepts:
And these are only formal definitions. You can dig deeper and discuss the rules of trust management of a mutual fund, security issues when working with such tools, the legal basis for their operation. Especially if we talk about Russian realities, which at times are very far from what is written in the law.
We could answer this question and "load" you with terms, definitions and information borrowed from authoritative online sources, but there is not much point in this.
Attention! A trust fund can be of two types: lifetime (it is valid until the death of the creator) or testamentary, when assets are transferred after the death of the creator!
Typical Trust Fund includes:
A trust fund can hold almost any type of asset - cash, securities, real estate, valuables, and even works of art. In some cases, a trust fund may control (contain, include) entire business structures that are actively involved in business operations. Simply put, a trust can accumulate any asset of value.
A trust fund is a legal entity. This means that the creator himself determines the rules for the transfer of assets and the mandatory conditions that must be met. This achieves a maximum level of control that other tools do not provide.
Typical examples are a ban on payments with the condition that the beneficiary cannot use the funds / assets to pay off a debt, reach a certain age, or any other conditions (marriage, birth of children, achievement of a certain social status or other conditions).
 What is P R bond?
27/11/2023
What is P R bond?
27/11/2023
 What is Compulsory Convertible Debentures?
27/11/2023
What is Compulsory Convertible Debentures?
27/11/2023
 Dynamics of Central Asian Economies
17/11/2023
Dynamics of Central Asian Economies
17/11/2023