Behind the abbreviation CFO, which stands for Chief Financial Officer, is the international name of the position of financial director. In most companies, it corresponds to the level of vice president or deputy general director for finance (Finance Vice President).
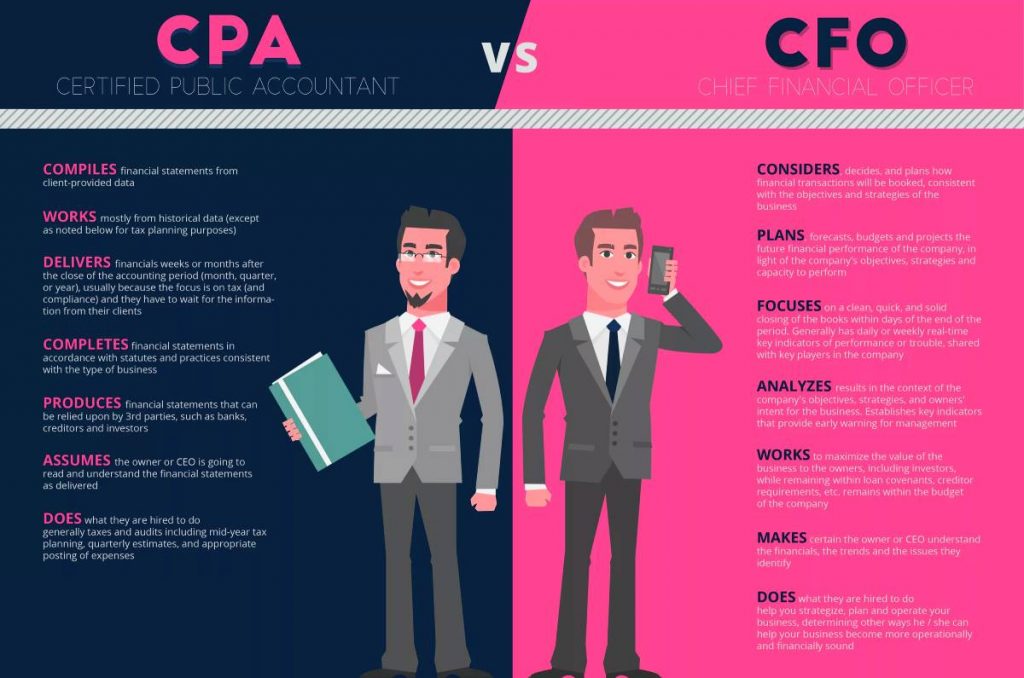
Sometimes people ask me what is the difference between a CFO and a CEO. Let's see what job titles are used today and for what.
First of all, abbreviated names are used for convenience, it is faster, but also to a greater extent they have come to us from the foreign labor market, where such abbreviations are the norm. The format for writing posts in this form is called CxO.
CFO is a right hand of the CEO and one of the key executives. It is he who is responsible for managing the company's finances, he is engaged in planning and is fully responsible for controlling the spending of finances and the execution of budgets. His area of responsibility is the financial policy and strategy of his functional area. It is he who, as a rule, is a member of the Board of Directors and takes the place of one of the Vice-Presidents of the Company.
And most importantly, as a rule, CxO managers have more resources and opportunities than just TOP managers. For example, they may be holders of options or shares of the enterprise. They may also have the right to sign and other powers that are not inherent in the Russian-language function.
If you occupy a managerial role or plan to develop to the level of a TOP manager, then it is simply necessary to navigate these abbreviations in order to speak the language of business.
The CFO (financial director) manages the financial division of the company (if it is allocated in a separate block). Often, the financial director manages the accounting department and the financial control unit. Thus, often the positions of chief accountant and CFO can be combined.

The employees of the internal audit and compliance department, as well as the corporate treasury (i.e., the unit responsible for corporate finance: working with banks, credit institutions, investors, managing liquidity, financial risks, etc.) are also directly subordinate to the CFO.
The CFO is also responsible for formulating the organization's financial plan (or budget) and making pricing decisions, for example. Therefore, as a rule, the budgeting department is directly subordinate to him.
Therefore, the CFO's area of responsibility includes the following areas of the company's activities:
This list is only a general list and is not final, since the financial director, who is the key figure in the enterprise after the general director, may also be responsible for a number of other issues and projects (depending on the specifics of the company's work), including those related to only directly to the financial, but also to the commercial and administrative sphere. After all, the financial director is directly responsible not only for the current financial result of the company, but also for its strategic development.
 What is P R bond?
27/11/2023
What is P R bond?
27/11/2023
 What is Compulsory Convertible Debentures?
27/11/2023
What is Compulsory Convertible Debentures?
27/11/2023
 Dynamics of Central Asian Economies
17/11/2023
Dynamics of Central Asian Economies
17/11/2023